Vishing
Spoofing a legitimate phone number, voice phishing scammers lead people to believe the call is legitimate
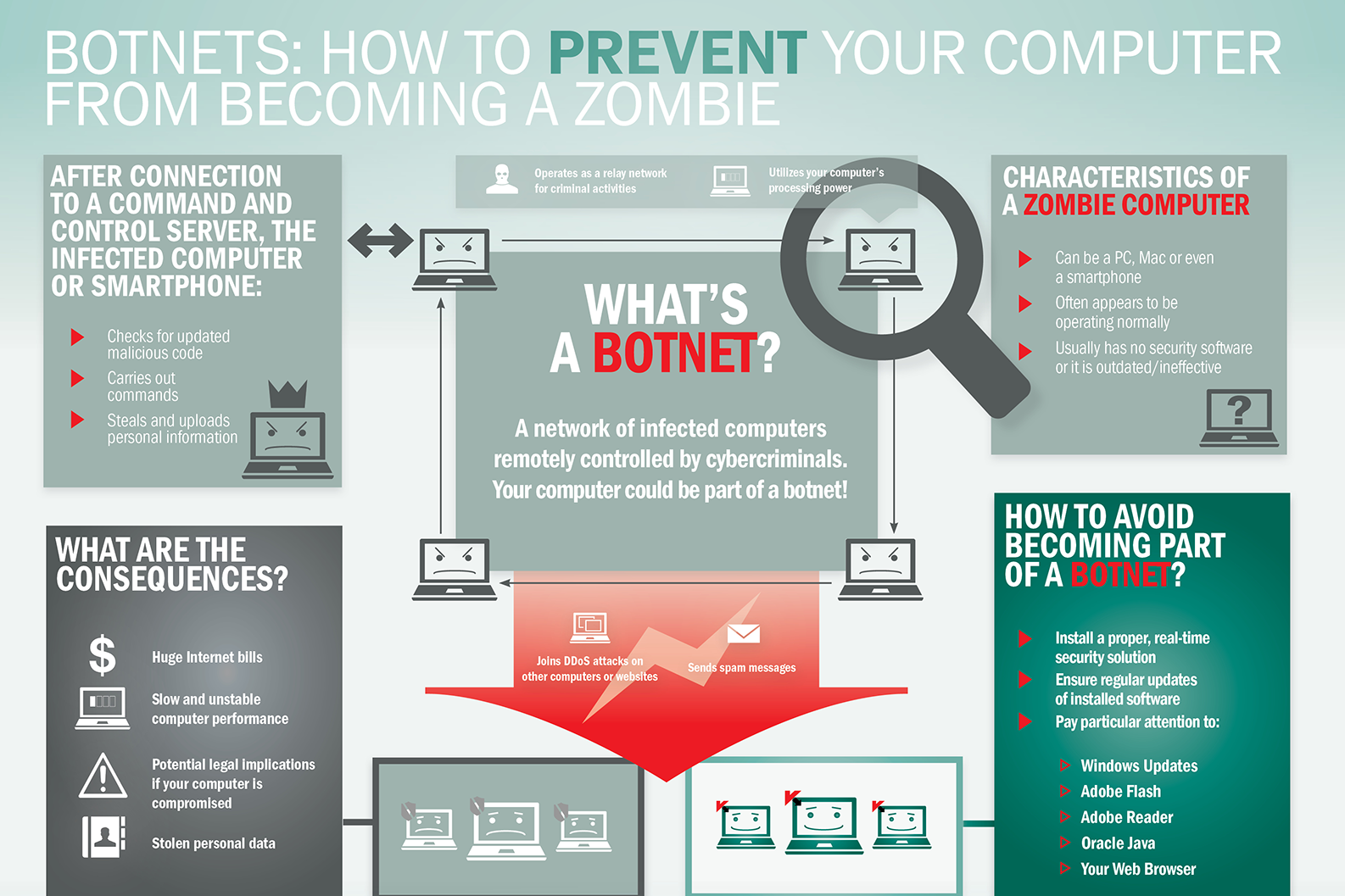
What is Vishing?
We’ve all heard the countless stories on phishing and how much of a threat is it in today’s information security landscape. Social engineering to solicit confidential information via email is a threat that all of us have been made aware of. Extensive efforts have been made to not only reduce the influx of phishing emails, but also to raise awareness so that users have the know-how to assess and respond to the threat when a malicious email hits their inbox.
In response, threat actors have turned to a newer form of exploitation: Vishing. Vishing is a form of criminal phone fraud that uses social engineering over the phone or SMS to gain confidential information. Here are some examples
Fake call from “Help Desk” asking for credentials
Unsolicited calls for credit and loans
Calls from a fake client asking about an invoice
Vishing is becoming an increasingly favored tool attackers use, due to the Covid-19 pandemic. With the shift to work-from-home environments, corporate VPNS, and elimination of in-person verification, threat actors are shifting their tactics to exploit this widespread weakness.
How do I protect my firm against Vishing?
Security awareness is the best line of defense against this type of attack, so be sure to incorporate vishing education into your information security awareness program. Policies and procedures should be established and communicated to ensure that employees can verify identity when the helpdesk or anyone else from the company calls and asks after proprietary topical information. It is imperative that information security managers instill a sense of suspicion for any caller asking for said information.
Enabling MFA for any system that has access to confidential information, network or system is non-negotiable; that second factor of authentication can halt many types of attacks. When you enable MFA you avoid the use of SMS as a means of authentication as SMS is easily manipulated and exploited.
Lastly, always apply least privilege so that in the event an account is compromised, there will be minimal damage.
AUTHOR: CARLOS NETO
Information Security Officer