What is Cybersecurity Awareness Month?
Cybersecurity Awareness Month was founded in 2004 as a collaborative effort between the government and private industries to raise awareness about digital security and empower everyone to protect their personal information from digital forms of crime. It also aims to increase the resiliency of the country during a cyber threat.
Cybersecurity Awareness makes the community more aware to recognize, reject and report threats. Organizations can protect their users from being scammed and safeguard the organization.
When is Cybersecurity Awareness Month?
October is known as National Cybersecurity awareness month. It's an international campaign.
What is the history behind Cybersecurity Awareness Month?
In 2004 the President of the United States and Congress declared October to be Cybersecurity Awareness Month, helping individuals protect themselves online as threats to technology and confidential data become more commonplace. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCA) lead a collaborative effort between government and industry to raise cybersecurity awareness nationally and internationally.
Facts and figures
42% of schools have students or employees that circumvent cybersecurity protections (Impact My Biz)
Nearly three-quarters (74%) of ransomware attacks on higher education institutions succeeded due to a lack of awareness (Inside Higher Ed)
Ransomware attacks on U.S. schools and colleges cost $6.62b in 2020 (darkreading)
95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. (World Economic Forum)
69% of Companies’ Are Increasing Their Investments in Their Cybersecurity Budgets (Global digital Trust insights report
APWG (Anti Phishing Working Group) Reports That Website Phishing Attacks Have Tripled Since Early 2020
88% of Businesses Experienced a Ransomware Attack
What are some examples of past Cyber-attacks?
The most recent well-known attack was the Colonial Pipeline (May 2021). The pipeline from Houston to the southeastern United States suffered a ransomware attack that took over key components of the computer software used to control the pipeline. This attack was singlehandedly the largest attack on oil and gas infrastructure in U.S. history. The attack led to panic buying of gasoline in the southeast, which caused shortages in some areas. Anthem (2015) a U.S. healthcare company, sustained what at the time was the biggest data breach in U.S. history. Hackers gained access to patient names, Social Security numbers, birthdays, addresses, emails, employment information and salary data.
The National Basketball Association (NBA) was hit with a cyberattack in 2021. In mid-April of 2021, the hacker group Babuk claimed to have stolen 500 GB of confidential data concerning the Houston Rockets. Babuk warned that these confidential documents, including financial info and contracts, would be made public if their demands were not met. As of this posting, no ransom payments have been made.
REvil, the same hacker group made headlines in July with an attack on Kaseya. Kaseya manages IT infrastructure for major companies worldwide. Similar to the attacks on Colonial Pipeline, this hack could potentially disrupt key areas of the economy on a large scale.
REvil carried out this attack by sending out a fake software update through Kaseya’s Virtual System Administrator, which infiltrated both Kaseya’s direct clients as well as their customers. According to REvil, one million systems were encrypted and held for ransom. Kayesa, stated that around 50 of their clients and around 1000 businesses were impacted. REvil demanded $70 million in bitcoin. To illustrate the impact of the cyber-attack, Coop, a Swedish supermarket chain, was forced to close 800 stores for a full week.
Soon after the attack, the FBI gained access to REvil’s servers and obtained the encryption keys to resolve the hack. Fortunately, no ransom was paid, and Kaseya could restore its clients' IT infrastructure. Although it started as one of the biggest ransomware attacks of the year, the situation was salvaged in the end.
How should you and others stay safe?
· Always use Antivirus
· For younger kids use Parental Controls
· Never download random files or software
· When you can Use Two factor authentication
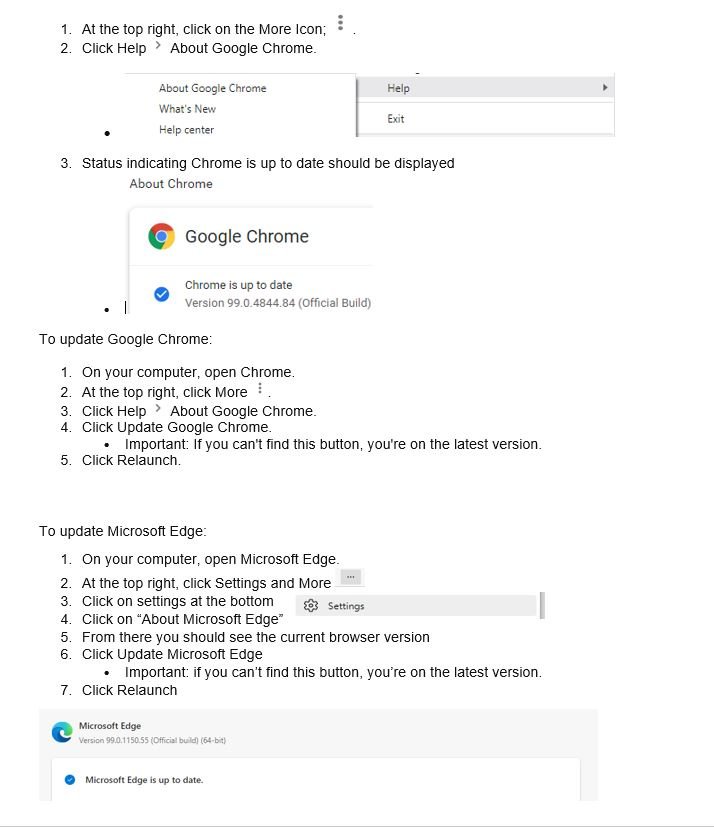
· Keep your software up to date
· Complex Passwords
· Don’t click on any links or attachments in texts, emails, or social media posts
· Don’t connect to unfamiliar Wi-Fi networks
· Only visit secure websites (HTTPS)
· Try not to overshare information (social media)
· Use a VPN